目前仅仅包括部分内容, 有翻译不准确或者错误的地方欢迎到 这里提 Issue 指正
OverView
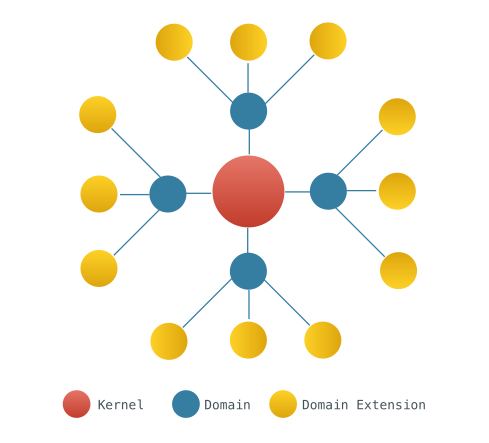
Mixin is composed of a single theoretically permanent Kernel, many dynamic Domains and different multipurpose Domain Extensions, to formulate an extended star topology.
Mixin 由 以下三部分组成, 共同构成一个 扩散型的 星型拓扑
- 一个理论上永久的 Kernel (内核)
github.com/MixinNetwork/mixin - 许多的可拔插的 Domain(域)
- 不同的用途的 Domain Extension (域扩展)
This topology may lead the concern that Mixin is a centrally controlled network, but that’s not the case because of how the Kernel itself works
这种拓扑结构 可能会让人们担忧 Mixin Network 是一个 中心化 的网络, 但事实上并非如此.
Mixin Kernelis a high performance distributed ledger and its sole responsibility is to verify asset transactions.Although
Mixin Kernelverifies asset transactions , it doesn’t produce any assets. All assets flow through theMixin KernelbyMixin Domains.
Mixin Kernel 是一种高性能的 分布式账本, 它的唯一任务就是 验证资产交易.
尽管 Mixin Kernel 会验证资产交易, 但它不会产生任何资产. 所有的资产均由 Mixin Domain 提供给 Kernel.
Each
Mixin Domainis also a distributed ledger, whose job is providing assets to theMixin Kernel. The assets may be those on Bitcoin, Ethereum or any other blockchains, or even central organizations like banks.While each
Mixin Domainis a Component to provide assets forMixin Kernel, theMixin Kernelitself is also a component in theMixin Domainto verify and govern its assets.
每个 Mixin Domain 也是一个 分布式账本 , 它的任务是向 Kernel 提供资产. 这些资产可能是 Bitcoin 或者 其他的数字货币, 甚至银行等的中心化机构.
每个 Mixin Domain 是为 Kernel 提供 资产的组件, 而 Kernel 本身也是 Domain 中用于 验证和管理其资产的组件.
unlike most existing gateway based solutions ,
Mixin KernelandMixin Domainsare all public available distributed ledgers, with no central authorities.From the
Mixin KerneltoMixin Domains, theMixin Networkis all about assets and transactions. TheMixin Domain Extensionis where the magic happens, whether for Ethereum contracts, EOS contracts, a distributed exchange on somewhat trusted instances, or anything else.
和绝大多数的基于网关的解决方案不同, Mixin Kernel 和 Domain 都是公开可用的, 不存在中心化管理.
从 Kernel 到 Domain , 所有的一切都是关于 资产 和 交易的. 但 Doamin Extension 则可以接入包括 Ethereum 智能合约 , EOS 合约, 或者其他的任何东西.
Mixin Kernel
The core of
Mixin Networkis theMixin Kernel, a fast asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerant directed acyclic graph to handle unspent transaction outputs within limited Kernel Nodes.
Mixin Network 的核心是 Mixin Kernel , 一个快速的 异步的 拜占庭容错的 有向无环图(DAG graph), 用于处理 有限个 Kernel 节点 中的 UTXO (unspent transaction outputs)
Ghost Output
Mixin Kernel utilizes the UTXO model of Bitcoin to handle transactions, and CryptoNote[0] one time key derivation algorithm to improve privacy, since there is no address reuse issue. We call the one time key a Ghost Address and the output associated with it a Ghost Output.
Mixin Kernel 使用 Bitcoin 的 UTXO 模型来处理交易, 由于不存在 转账地址重用问题, 所以选择 使用 CryptoNote 中提出的 一次性密钥 推导算法 来提高隐私性. 我们将这里得到的 一次性密钥称为 Ghost Address, 并将与其相关的输出 称为 "Ghost Output"
In the algorithm, each private user key is a pair (a, b) of two different elliptic curve keys, and the public user key is the pair (A, B) of two public elliptic curve keys derived from (a, b).
在这个算法中, 每个用户的 私有身份密钥 是来自两个不同的椭圆曲线的两个密钥组成一对 (a,b), 公有身份密钥是由 私有身份密钥(a,b) 导出的两个 公有椭圆曲线密钥组成一对 (A,B)
When Alice wants to send a payment to Bob, she gets Bob’s public user key (A, B) and derives at least three Ghost Addresses with some random data, which ensures at least three different Ghost Outputs will be created for Bob.
The three Ghost Outputs threshold delivers better privacy, and also forces the outputs random amounts.
After deriving the Ghost Addresses, Alice will sign the transaction with CryptoNote algorithm.
当 Alice 要向 Bob 发送一笔款项时, Alice 首先会得到 Bob 的公共身份密钥 (A,B), 并通过一组随机数据 推导出 至少三个 Ghost Address , 这也就保证了至少会为 Bob 创建三个不同的 Ghost Output
这至少三个 Ghost Output 为交易 提供了更好的隐私性, 并且强制输出随机金额.
在推导出 Ghost Address 后, Alice 将使用 CryptoNote 算法签名交易.
以下两幅图来自 CryptoNote 白皮书, 交易过程细节的中文翻译可以参考 Cryptonote 白皮书 中文翻译
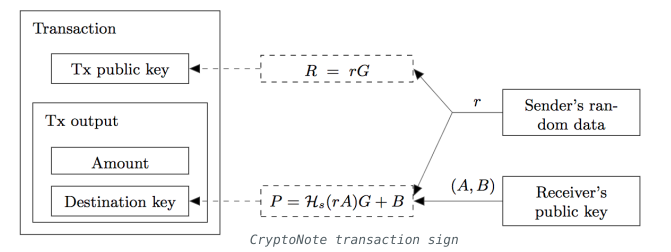
Note that, to improve privacy, Alice is forced to pick random UTXOs as the transaction inputs. After the transaction is signed, Alice sends it to the Mixin Kernel.
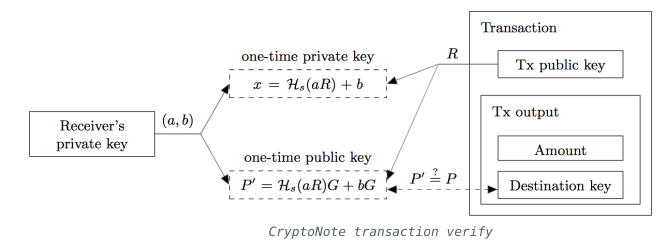
Only Bob can recognize his transactions due to the Ghost Address feature, he can decrypt the output information with his tracing key (a, B).
If an exchange wants to have a transparent address to disclose all its assets information publicly, it can just publish its tracing key (a, B) so that everybody can recognize all its transactions but can’t spend them without the secret key b.
需要注意的是, 为了提高隐私性, Alice 会被强制要求 随机选择若干 UTXO 作为 交易的 Inputs. 交易签名后, Alice 将其发送给 Mixin Kernel.
由于 Ghost Address 和 CryptoNote 的作用下, 只有 Bob 的 私有身份密钥 可以识别 Alice 的这笔交易, Bob 可以用它的 追踪密钥 (a,B) 解密输出信息.
如果一个交易所 想要有一个透明的地址, 来披露它的所有资产信息, 那么他可以直接公布它的 追踪密钥 (a,B) , 这样大家就可以识别它的所有交易, 但由于没有密钥 b , 所以就无法使用这个地址的资产进行交易.
Asynchronous BFT Graph (异步 拜占庭容错图)
Each Mixin Kernel Node is required to pledge 10,000 XIN, therefore due to the 500,000 XIN circulating supply[0], no more than 50 Kernel Nodes will exist. To prevent extremely centralized authority, the Kernel can only be booted with at least 7 Kernel Nodes.
The Kernel nodes make up a loose mesh topology, and are responsible for transaction validation and persistence. Unlike a blockchain, there are no blocks in the Mixin Kernel, all transactions will be exponentially broadcasted as soon as possible.
每个 Mixin Kernel 节点 需要抵押 10k XIN 代币, 由于在一开始只供应 500k XIN 代币, 所以在一开始 Kernel 节点不会超过 50 个. 也为了防止权力过于集中, Kernel 至少需要 7 个节点才可以启动.
Kernel 节点组成了一个 松散的网状拓扑结构, 并负责进行交易的验证和存储. 与 别的区块链中的 区块不同, Mixin Kernel 中没有那么强的区块的概念 (比方说 Bitcoin), 所有的交易都会尽快广播然后扩散到所有节点, 被广播的节点数呈指数化增长.
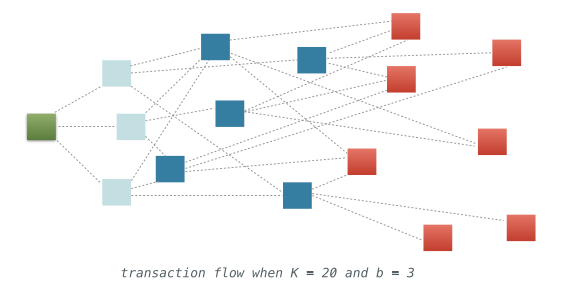
A typical Mixin Kernel transaction finalization sequence goes as follows:
- When Alice’s signed transaction is sent to the Mixin Kernel with K (7 <= K < 50) nodes, b (b > 1) random nodes (A) will receive it.
- Each node does the same transaction validation.
- Inputs are all unspent.
- Input and output amounts are in valid range.
- Verify the signature of each input.
- The total of input amounts equal to the total of outputs.
一个通常的 Mixin Kernel 交易从开始到结束的流程如下:
- 当 Alice 签名交易被发送到具有
K(7<= K < 50) 个节点的 Mixin Kernel 时,b个(b >1) 随机节点将接受到这笔交易 - 每个节点都会进行相同的交易验证
- 所有的 Inputs 都是 未被消费的 (unspent)
- Input 金额 和 Output 金额 都在有效的范围内
- 验证每笔交易的签名
- 所有 Input 的金额总和 等于所有 Output 的金额总和
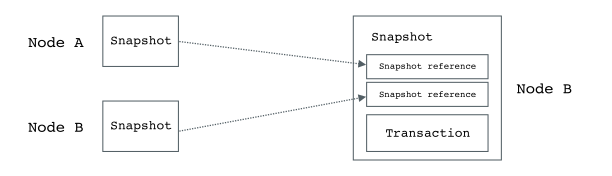
- Each node will create a Kernel Snapshot with the validated transaction, and the snapshot is the base unit stored in the Kernel to construct a DAG. Each snapshot is composed of:
- The transaction as payload.
- Previous snapshot hash of this node.
- The node signature.
- The signed snapshot will be broadcasted to another b random nodes (B) as soon as possible. After received the snapshot and validated with the same procedure in step 2, a new snapshot will be created immediately. This snapshot has the same payload as received snapshot, and the referenced snapshot hash is a pair of previous snapshot hash in this node and the received snapshot hash.
- Steps 4 will be repeated until the node learnt that wether the transaction is approved or rejected by at least 2/3K nodes. Since each snapshot referenced the parents up until the nodes group A, it’s easy for new nodes to learn that the previous snapshots are aware of the snapshots. This procedure can avoid lots of redundant works.
- In this procedure, a transaction can be approved or rejected in about K/b^2 rounds on average, considering the typical Kernel size, the latency may be within a single second with very high probability and guaranteed within seconds.
Due to the asynchronous BFT consensus, double spend is impossible. Because of the UTXO nature, snapshots order is irrelevant and high concurrency can be guaranteed in the DAG.
- 所有的节点都会用验证过的 交易信息 创建一个
Kernel Snapshot (内核快照), Snapshot 是存储在 Kernel 节点中, 构建 DAG 的基本单位. 每个 Snapshot 由以下几个部分组成:- 交易信息作为 Payload (主要内容)
- 该 Node 的上一个区块 Hash 信息
- 节点签名
- 签署的快照将尽快广播到另一个随机 B 节点. 在 B 节点收到 Snapshot 后, 将用
步骤 2中相同的过程进行验证, 完毕后将立刻创建一个新的 Snapshot, 节点 B 的 Snapshot 将由以下几个部分组成.- 这个 Snapshot 的 Payload (主要内容) 是收到 Snapshot 全文,
- 引用的 Snaphash Hash 与收到的 Snapshot 的 Hash 一样,
- Node 签名使用本节点的签名.
步骤 4将不断的在 Kernel 节点中重复进行, 直到 Node B 得知该交易被 2/3 的 Node 批准或者 拒绝. 由于每个 Snapshot 都引用了 接收到的 Snapshot , 所以可以追溯到 交易发生的第一个节点 A. 新的被传播到的节点, 很容易直到此前的快照的传播路径. 利用这个特性可以在开发中避免大量的冗余工作.- 在这个过程中, 通常
K/(b^2)就可以批准或者拒绝一笔交易, 如果按照通常的集群规模考虑, 那么每笔交易延迟大概率在 一秒之内, 最迟也会在几秒之内完成.
Due to the asynchronous BFT consensus, double spend is impossible. Because of the UTXO nature, snapshots order is irrelevant and high concurrency can be guaranteed in the DAG.
通过 异步的 拜占庭容错达成的共识的过程中, 双花交易 是不可能发生的. 也由于 UTXO 的特性, Snapshot 的顺序并不会影响 交易结果, 所以 有向无环图 中可以保证高并发.
Punitive PoS (惩罚性 PoS)
Each Mixin Kernel node takes 10,000 XIN, which is approximate 2% of the network stake. The Kernel can only operate with at least 7 nodes joined, or about 15% of the whole network stake.
每个 Mixin Kernel 节点需要质押 10k XIN 代币, 约占整个网络代币数量的 2% , Mixin Network 最少需要 7 个 Kernel 节点才可以正常运行, 整体质押 XIN 代币数量约占整个网络代币数量的 15%.
The Kernel BFT consensus is secured by a strict punitive PoS, if a Kernel Node is determined to be an attacker, all its collateral will be recycled to the mining pool. The node will be identified as an attacker if it tried to broadcast an obvious double spend snapshot. A snapshot will be considered obvious when some of its inputs state have been validated by at least 2/3K nodes.
内核 BFT 共识 是通过严格的 惩罚性 PoS 来保证的, 如果 Kernel 节点尝试 传播 一些 Input 已经被 2/3 的节点验证的 双花 Snapshot , 那么这个 Kernel 节点将被确定为攻击者. 这个 Kernel 抵押的所有 XIN 代币 都将回收到矿池.
The first time a node sends out an attacking snapshot, its stake won’t be recycled, but it will be flagged by the network as a potential attacker. The Kernel size will be temporally reduced to K - 1, with this reduction invisible to the potential attacker.
当 Kernel 节点第一次发出 被认为是 攻击的 Snapshot 时, 这个节点抵押的 XIN 代币不会立刻被回收, 但会被网络标记为 潜在攻击者. Kernel 节点数量 将暂时减少到 K-1 , 这种变化对 潜在攻击者 是不可见的.
All other nodes will still broadcast to the flagged node, but won’t consider its snapshots in stake votes. If further snapshots from the flagged node remain malicious, the Kernel will sign a snapshot with a transaction that will transfer all the flagged node’s collateral to the mining pool.
所有 Kernel 节点仍然会向 这个被标记 的 Kernel 节点广播 Snpashot, 但不会在 stake votes 中考虑这个节点提供的 Snapshot. 如果 被标记的 Kernel 节点 接下来的快照仍然被认为是 恶意的, 那么 Kernel 们将签署一份特殊的 Snapshot , 将 被标记节点 质押的全部 XIN 代币转移到 矿池.
The flagged node will be permanently removed from the Kernel and it will have some period to appeal to Mixin Kernel Governance[0], which is voted by all XIN holders.
被标记的 Kernel 节点 将永久的从 Kernel 中消除, 它的持有方 将有一段时间来进行申诉.
Trusted Execution Environment (TEE 可信执行环境)
Mixin Kernel is already an
ABFT(asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance)consensus DAG. To ensure further security, Kernel nodes must run in Trusted Execution Environment[1]. Specifically, Mixin uses Intel SGX[2] as the TEE implementation.
Mixin Kernel 已经是 异步拜占庭容错共识 的 DAG. 为了进一步确保安全. Kernel 的节点程序 必须在 可信执行环境(TEE) 中运行. 具体来说, Mixin 程序使用 Intel SGX 来作为 可信执行环境 的实现.
The TEE enforcement ensures three important security and trust factors in Mixin Kernel.
- All Kernel nodes should run the same consensus ruleset.
- Mixin Kernel will be trusted due to the Intel SGX enclave, even when the Kernel is controlled by several earlier Kernel nodes.
- Distributed Domain communications will be much more secure.
The underlying logic for the TEE security is that Intel SGX is somewhat trusted for the Mixin system.
Note that, Mixin Kernel is secure by itself, at least as secure as existing BFT solutions. The mandatory Intel SGX just makes it better.
Mixin Kernel 程序使用 TEE 的意义在于 如下三个因素,
- 所有的
Kernel 进程都应该运行在相同的环境中. Mixin Kernel 进程可以因为运行在 Intel SGX 这块飞地中, 而被认为是可信任的. 即便 Kernel 在早期只有几个节点.- 分布式域通信 (Distributed Domain communications) 将更加安全
可信执行环境 能提供 安全性的基本逻辑是,对于 Mixin 而言,Intel SGX 被认为是值得信赖的.
但也请注意, Mixin Kernel 本身是安全的, 至少和现有的 BFT 方案一样安全. 强制的 Intel SGX 只是让它变得更好.
Light Witness Node (轻量观察节点)
Mixin Light node is a simplified payment verification (SPV) node to Mixin Kernel. It typically stores all its unspent outputs for easy account balance query.
If the Light node is a XIN holder, it has the chance to act as a Light Witness. The Light Witness will actively monitor the Mixin Kernel, and will be scheduled to vote automatically on the attacker appeals.
Mixin Light 节点是 Mixin Kernel 的 简化支付验证 (SPV) 节点. 它通常会保存所有 UTXO 来方便账户余额查询.
如果 Light Node 持有 XIN 代币, 那么它就有机会充当 Light Witness 节点 , Light Witness 会主动监控 Mixin Kernel , 并会被安排对攻击者的申诉进行自动投票.
The Light Witness vote is weighted on their XIN stake. And the vote is mostly on the attacker node’s network connectivity state to determine whether the attacker behavior is caused due to network delay.
All the Light Witness votes will be weight calculated with the Mixin Kernel Governance votes, to determine the final attacker appeal. If the appeal fails, the penalty will be final.
The Light Witness is incentivized to do these votes because they could get the mining reward if they do some work for the network itself.
Light Witeness 的投票权重 是根据它们质押的 XIN 代币来决定的. 而投票的点是 根据攻击者 Kernel 节点的网络连接状态来判断, 这次攻击是否由网络延迟造成.
所有的 Light Witness 节点 票数 和 Mixin Kernel 的治理票数 进行加权计算, 来最终判定 攻击者是否上诉成功. 如果上诉失败, 则执行最终惩罚.
为了让 Light Witness 有动力去做这些投票, 会根据 这些 Light Witness 的贡献来提供一定的挖矿奖励.
Mixin Domain
Mixin Domain is a distributed ledger to provide assets for the Mixin Kernel. The assets may be those on Bitcoin, Ethereum or any other blockchains, even central organizations like banks.
Mixin Domain 是一个分布式账本, 用于 为 Mixin Kernel 提供资产. 这些资产可能是 Bitcoin 等.
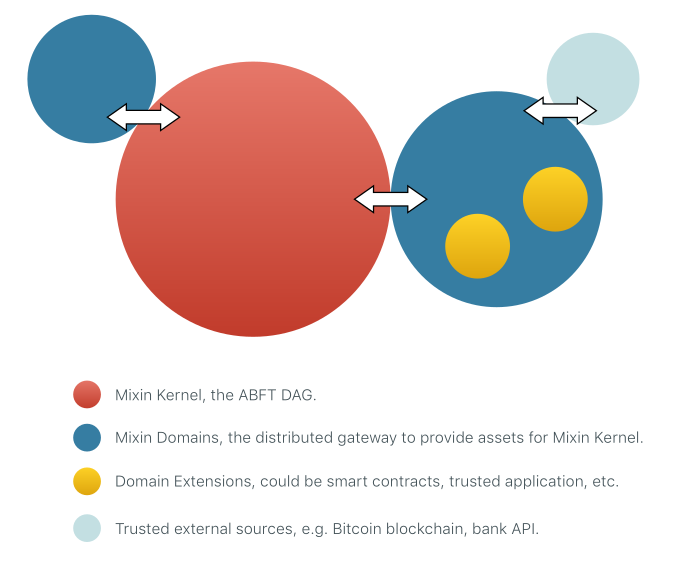
图示翻译:
- 红色代表 Mixin Kernel , 一个 异步,拜占庭容错共识 的 DAG
- 深蓝色代表 Mixin Domains, 一个分布式的网关, 用于提供 资产给 Mixin Kernel
- 黄色代表 Domain Extensions, 可以是 智能合约, 或者 可信应用 等.
- 浅蓝色代表 可信的外部实体, 例如 Bitcoin , 银行 API
Kernel System Calls
Mixin Kernel offers some system calls to communicate with Domains, and it’s the only way the Kernel and Domains can exchange state. The system calls are defined as standard JSON-RPC interfaces.
Mixin Kernel 提供了一些 系统调用 来与 Domain 进行通信, 这是 Kernel 和 Domain 交换信息的唯一方式. 这些系统调用被定义为 标准的 JSON-RPC 接口.
JSON-RPC is a stateless, light-weight remote procedure call (RPC) protocol. It is transport agnostic in that the concepts can be used within the same process, over sockets, over HTTP, or in many various message passing environments. It uses JSON (RFC 4627) as data format.
Currently Mixin Kernel only implements the standard HTTPS transport for the protocol, and the available calls are listed below.
JSON-RPC 是一种 无状态 且轻量的 RPC 协议. 协议层 与 传输层 无关, 可以在任意一种传输层中使用 JSON-RPC 协议, 例如 HTTP 或者 Socket 通信 等. 它使用 JSON (RFC 4627) 作为数据格式.
目前 Mixin Kernel 仅实现也仅支持 标准的 HTTPS 传输层 来承载 JSON-RPC 协议, 下面列出了可用的接口.
kernel_registerDomain (注册 Domain)
Register the Domain and waiting for the Kernel approval to connect. The call can also update the domain nodes. The registered domain will be forced to form a XIN stake based network between the domain nodes and the Kernel as a whole.
The domain registration is a governance behavior, and should relate to the domain nodes XIN stake. In the future, we hope to implement a more automatic domain management policy in Mixin Kernel. The upgrade policy should always be governed by all Kernel Nodes and XIN holders.
Note that, all Kernel System Calls should be forwarded to b known Kernel Nodes to ensure delivery.
注册 Domain 到 Mixin Kernel 并等待审核 才能够连接. 这个调用也可以用于 更新 Domain 的节点. 注册完毕的 Domain 将被迫在 Domain 节点 和 整个 Kernel 之间形成一个 基于 XIN 质押的网络.
Domain 注册是一种治理行为. 应该与 Domain 节点的 XIN 代币质押有关. 将来我们希望能够在 Mixin Kernel 中实施 更加自动的 Domain 管理策略. 升级策略应该始终有所有的 Kernel 节点和 XIN 代币的持有者们共同治理.
注意, 所有的 Kernel System Call 都需要转发到 b 个已知的 Kernel 节点上以确保提交.
Detail
func kernel_registerDomain(uuid string, publicKeyList []string ) (res string)
Parameters
- UUID -
一个唯一的 UUID, 作为这个 Domain 的 ID.A unique UUID that represents the domain among all other domains. - Array -
Domain 节点的 公钥列表..Array of domain nodes’ transparent public keys.
params: [“c6d0c728-2624-429b-8e0d-d9d19b6592fa”,[“4b7a842ce6050c99450dc30b4e848c4eaffd33915653b472d900f47d11722058”,“b3aef7b3a998a593c157103d20f9cb17bdbd535f304b17c862e3b35b108faeb8”]]
Returns
String - Indicate th e registration request state, the value is one of invalid, pending, denied, and approved.
String - 返回一个 表示注册请求的状态, 它的值为 invalid(无效), pending(待定),denied(拒绝), approved(批准) 中的一个
Standard Domain Interfaces (标准 Domain 接口)
A domain can only be registered to the Mixin Kernel if it implements all the Standard Domain Interfaces.
只有实现了全部 Standard Domain Interface 的 Domain 才能够注册到 Mixin Kernel 上
domain_getKeyDerivationFunction (获取密钥生成函数)
Get the domain specific asset key derivation function, which is one of some key derivation methods in Mixin Kernel, and could be upgraded with governance.
The supported methods may also be extended to some sandboxed VM languages such as solidity.
用于 Kernel 获取 Domain 生成资产密钥的方法参数 的接口, 这是 Mixin Kernel 中的一些 密钥生成方法之一, 可以通过治理升级.
支持的方法也可以其他扩展到别的 沙箱虚拟机语言, 例如 Solidity.
Overview
type Res struct{
Method string
params []interface{}{}
}
func domain_getKeyDerivationFunction(uuid string) (res Res)
Parameters
- UUID -
一个唯一的 UUID,资产 ID.The global unique asset ID in the whole Mixin Network.
Returns
Object - 方法名和参数 The function name and parameters.
- method: String -
函数名The function name, one of the predefined derivation function names in Kernel. - params: Array -
参数调用这个方法需要传入的参数. The parameters should be used relative to the method.
domain_associatePublicKey(关联 Public Key)
Associate a Mixin public key to the domain for an asset supported by the domain. The public key and domain asset association is the magic that will associate an external asset to the Mixin Kernel.
After public key associated with an asset, it will get an asset specific public key, e.g. Bitcoin public key.
Whenever the Bitcoin blockchain has an output to this public key, the domain will create a transaction to the Mixin public key.
将一个 Mixin 公钥 关联到 Domain, 以获得这个公钥在 Domain 中关联的资产列表. 公钥和 Domain 的资产关联 是将 外部资产关联到 Mixin Kernel 的关键.
将 公钥与资产关联后, 会得到一个 资产特定的公钥, 例如 Bitcoin 公钥.
每当 Bitcoin 区块链上有交易发送到这个 Bitcoin 公钥上, 那么Domain 就会创建一条交易, 发送到这个 Mixin 公钥上
This works because the Mixin Kernel and the Mixin Domain is also a Proof of Stake network. Besides the XIN collateral, there are also additional Intel SGX enforcement for all related functions.
After the domain create the asset transaction to the public key, the asset will be locked by both the Mixin Kernel and Mixin Domain. This result in a corresponding asset lightning transaction in Mixin Kernel.
之所以这样, 是应为 Mixin Kernel 和 Mixin Domain 也是一个 PoS 网络. 除了 XIN 代币 作为抵押, 还有额外的 Intel SGX 执行所有相关功能.
Domain 创建资产交易到公钥后, 资产会被 Mixin Kernel 和 Mixin Domain 同时锁定. 这样就会在 Mixin Kernel 中产生相应的资产的闪电交易.
Overview
func domain_associatePublicKey(publicKey string, uuid string) (specificPublicKey string)
Parameters
- String -
一个 Mixin 公钥The Mixin public key. - UUID -
资产 IdUnique asset ID within the whole Mixin Network.
params:
[“4b7a842ce6050c99450dc30b4e848c4eaffd33915653b472d900f47d11722058”, “c6d0c728-2624-429b-8e0d-d9d19b6592fa”]
Returns
String - 与Mixin公钥关联的资产特定公钥. The asset specific public key associated with the Mixin public key.
domain_unlockAsset (解锁资产)
Unlock the asset and transfer out to external sources, this is similar to the withdrawal action on a crypto asset exchange.
The operation to unlock is somewhat similar to the associate function, it must be signed by both the Mixin Kernel and Mixin Domain to make it a valid snapshot acceptable by the network.
解锁 和 转出 外部资产, 这类似于 在交易所的提币操作.
解锁(unlockAsset)操作和上面的关联(associatePublicKey)操作有些类似, 必须由 Mixin 内核 和 Mixin Domain 签名, 以使其成为一个 网络上的一个 Snapshot.
Overview
func domain_unlockAsset(assetUuid UUID, specificPublicKey string,amount string,fee string) (identifier string)
Parameters
- Uuid -
资产 UUIDUnique asset ID within the whole Mixin Network. - String -
外部资产专用公钥External asset specific public key. - String -
解锁的资产金额The amount of asset to unlock. - String -
转账费率The fee for external source transaction.
params: [“c6d0c728-2624-429b-8e0d-d9d19b6592fa”,“15SdoFCiwaoUN4grnhPCoDWxWLcY6ZT68V”, “12.345678”,“0.0005”]
Returns
String - 外部来源交易标识符, 例如 Transaction hash The external sources transaction identifier, e.g. transaction hash.
The above three Domain Interfaces are mandatory for all domains to be approved by the Kernel. They communicate through the Intel SGX trusted transport layer, and all encrypted private keys are securely duplicated in all Kernel Nodes and Domain Nodes.
每一个加入 Mixin Network 的 Domain 都需要实现以上三个方法. 他们通过 Intel SGX 来进行受信任的通信, 并且所有私钥都在加密后保存在 Mixin Kernel 节点 和 Domain 节点上.
Domain Extensions
With a transaction only purpose Mixin Kernel, and Mixin Domains as assets provider and gateway to external blockchains or any other sources, Mixin has become the most sophistic and high performance distributed ledger to almost all digital assets.
However, people need smart contracts, which have been made popular by Ethereum. We allow Extensions to Mixin Domains, something similar to smart contract but with higher robustness, capability and performance.
Domain Extensions are programs running in the Domain Virtual Machine secured by the Secure Enclave in Intel SGX, a popular and secure Trusted Execution Environment.
通过仅仅将 Mixin Kernel 作为交易目的, 以及 将 Mixin Domains 作为资产提供者和 外部资产网关. Mixin 成为了几乎所有数字资产的分布式账本, 这个账本复杂而又高性能.
但是, 人们需要智能合约, Ethereum 上的智能合约已经开始流行. 我们通过 Mixin Domains Extensions, 来实现类似智能合约的功能. 但这具有更高的鲁棒性, 可塑性 和 性能.
Domain Extensions 是在 Domain 虚拟机中运行的程序, 这个 Domain 虚拟机受 Intel SGX 中的 Secure Enclave 保护
Due to the possibility to run the “smart contract” in a single computation unit, Domain Extensions can achieve many goals which are almost impossible in something similar to Ethereum.
Much higher performance and lower latency which is only limited by the hardware.
Non-deterministic transactions, e.g. trustable random number.
Interact directly with trusted external sources.
Besides these trusted applications, it’s also possible to run other popular distributed VM, e.g. Ethereum or EOS.
由于可以在单个计算单元中运行 “智能合约”, 因此 Domain Extensions 可以实现许多功能, 而这在类似于 Ethereum 的应用中几乎是不可能的.
- 更高的性能和更低的延迟,仅受硬件限制.
- 非确定性交易, 例如可信任的随机数(
译者注: Ethereum 网络由于公开运行, 随机数比较容易受到攻击) - 直接与受信任的外部资产进行交互.
除了这些受信任的应用程序之外,还可以运行其他流行的分布式虚拟机,例如 Ethereum 或 EOS
Attack Resistance
暂不翻译
Governance
暂不翻译
XIN - The Token
暂不翻译
Conclusion
暂不翻译

 Cryptonote
Cryptonote